Services
TIP
During this tutorial you'll learn how to manage Services on Kubernetes.
- Level: beginner
- Requirements: none
- Previous Tutorials: deployments
- Can run on Cluster: any, GKE
- Can run on Namespace: any
- Images used:
nginx:alpine
Services are an abstract way to expose an application running on a set of Pods as a network service.
Nginx Deployment
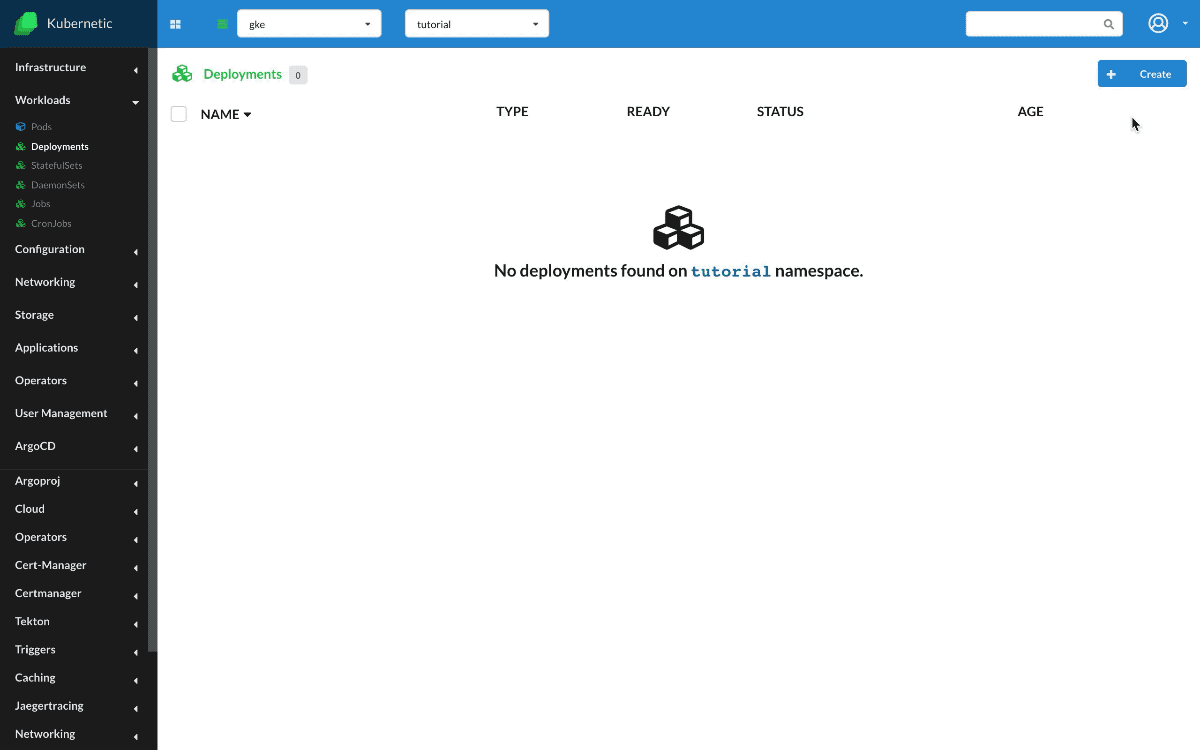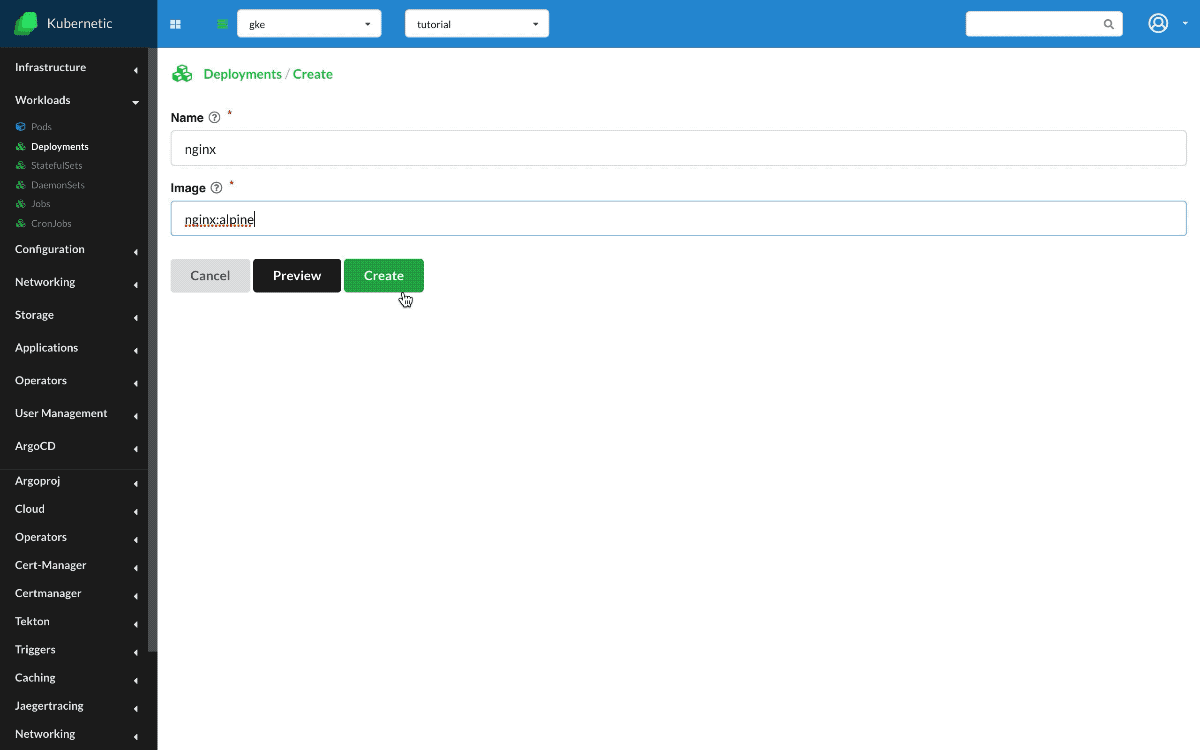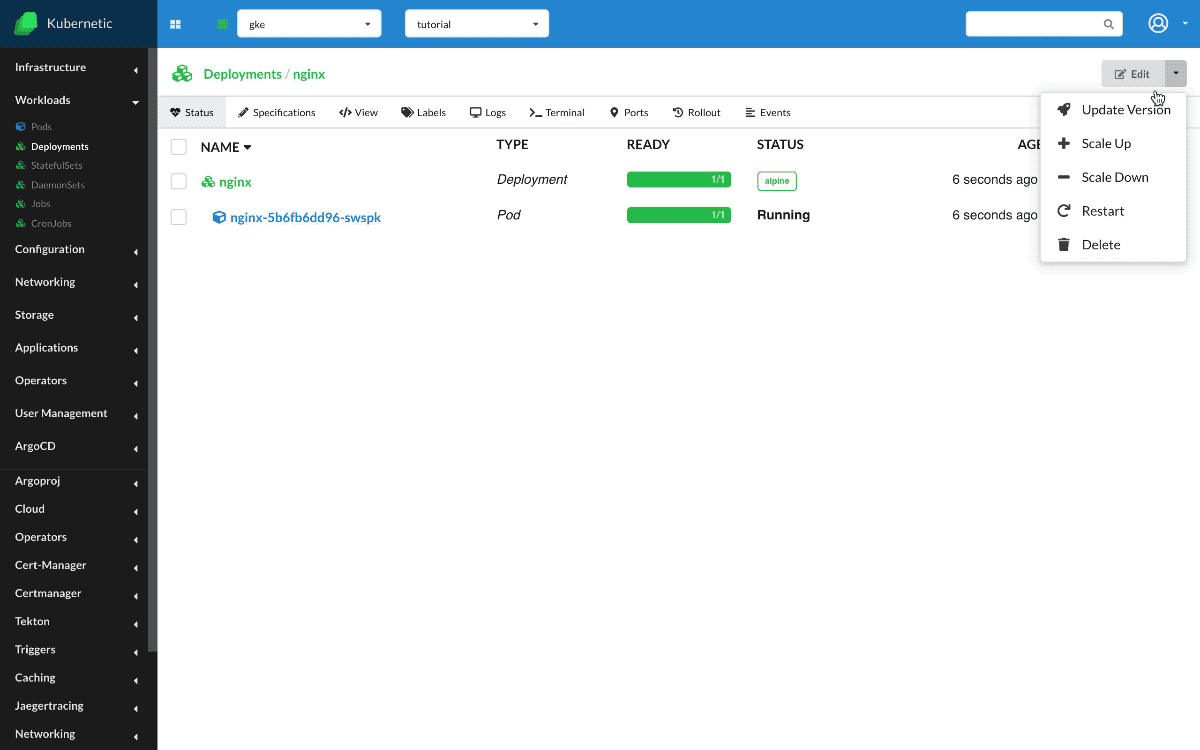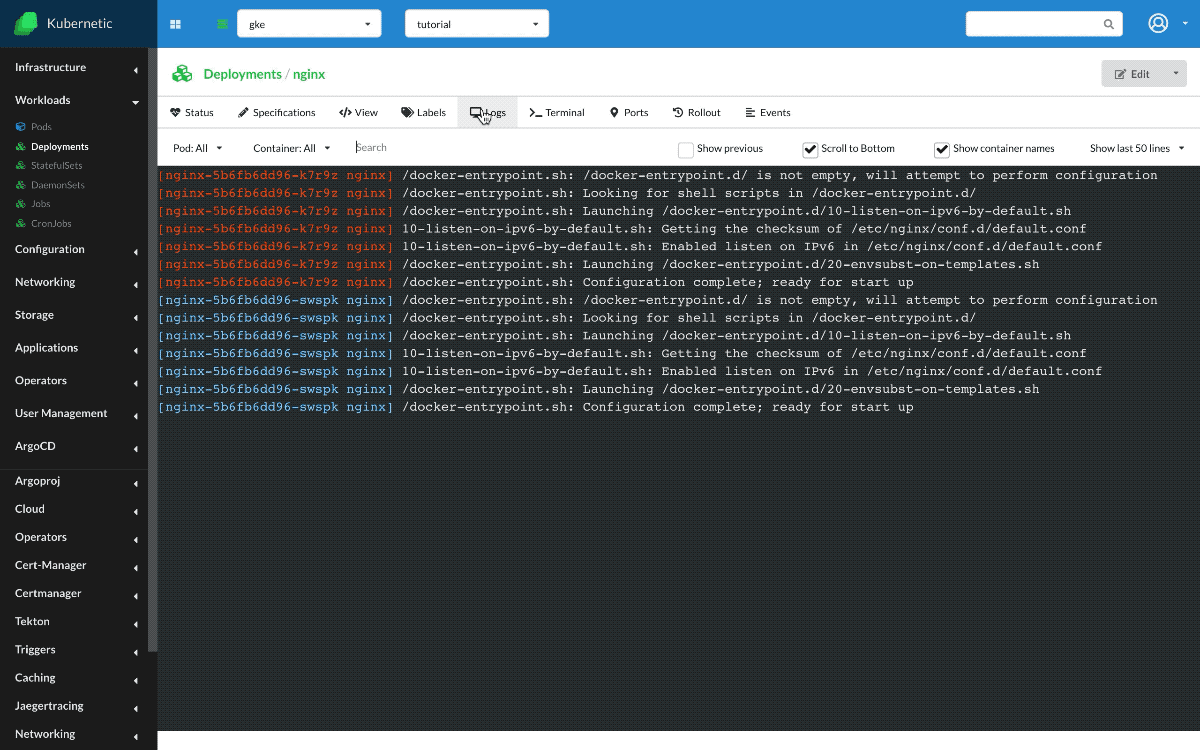
- Create:
Deployment- Name:
nginx - Image:
nginx:alpine
- Name:
A Service connects a set of pre-existing Pods by using the .spec.selector field. Before creating a Service we need to already have running pods with the proper labels. In Kubernetic, same as with kubectl create commands, the label app is filled with the resource name as unique selector. So by creating a Deployment and Service with the same name they will share the same label selector and connect.
So, first create a Deployment with name nginx and image nginx:alpine which runs an nginx web server, and scale up to two instances.
Nginx ClusterIP Service
- Create:
Service- Name:
nginx - Type:
ClusterIP - Paths:
- Port:
80 - Target Port:
80
- Port:
- Name:
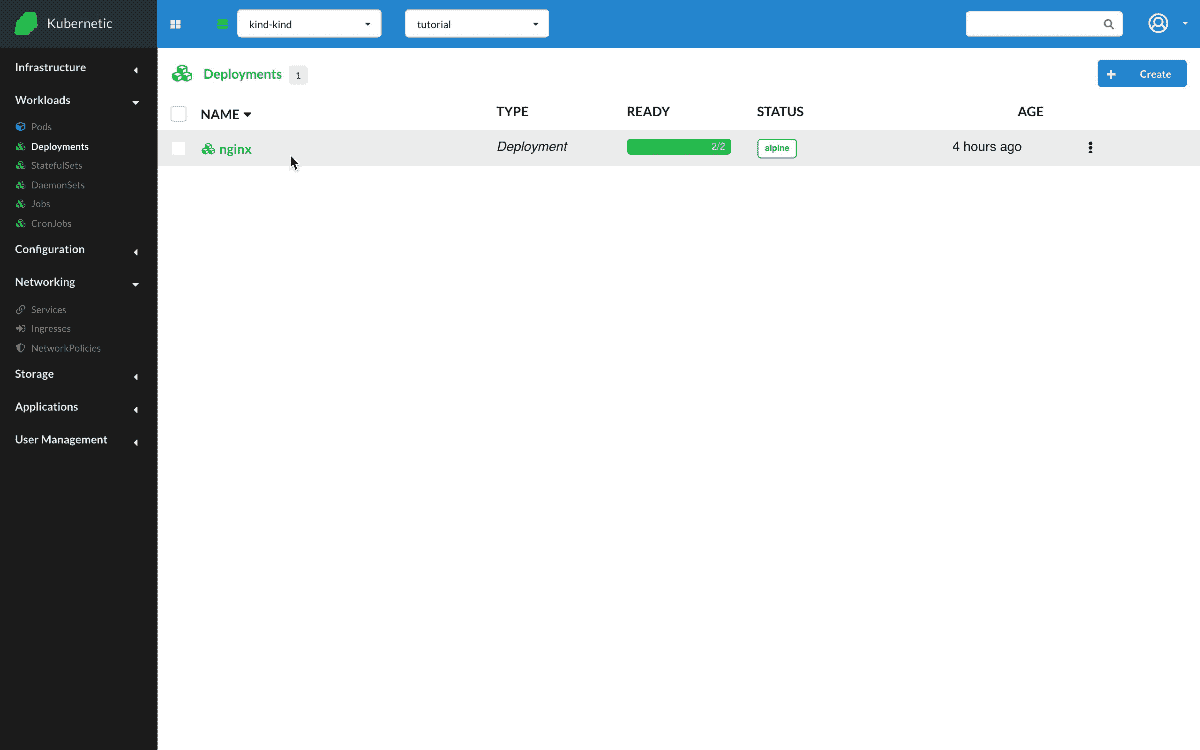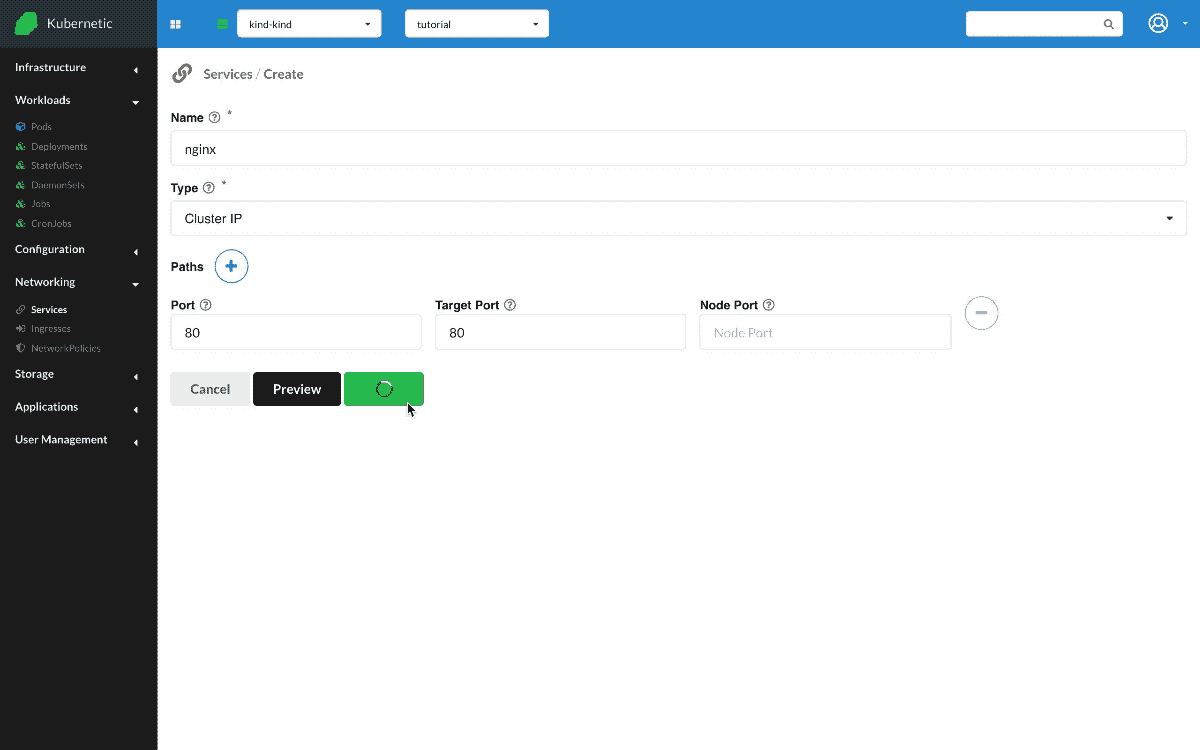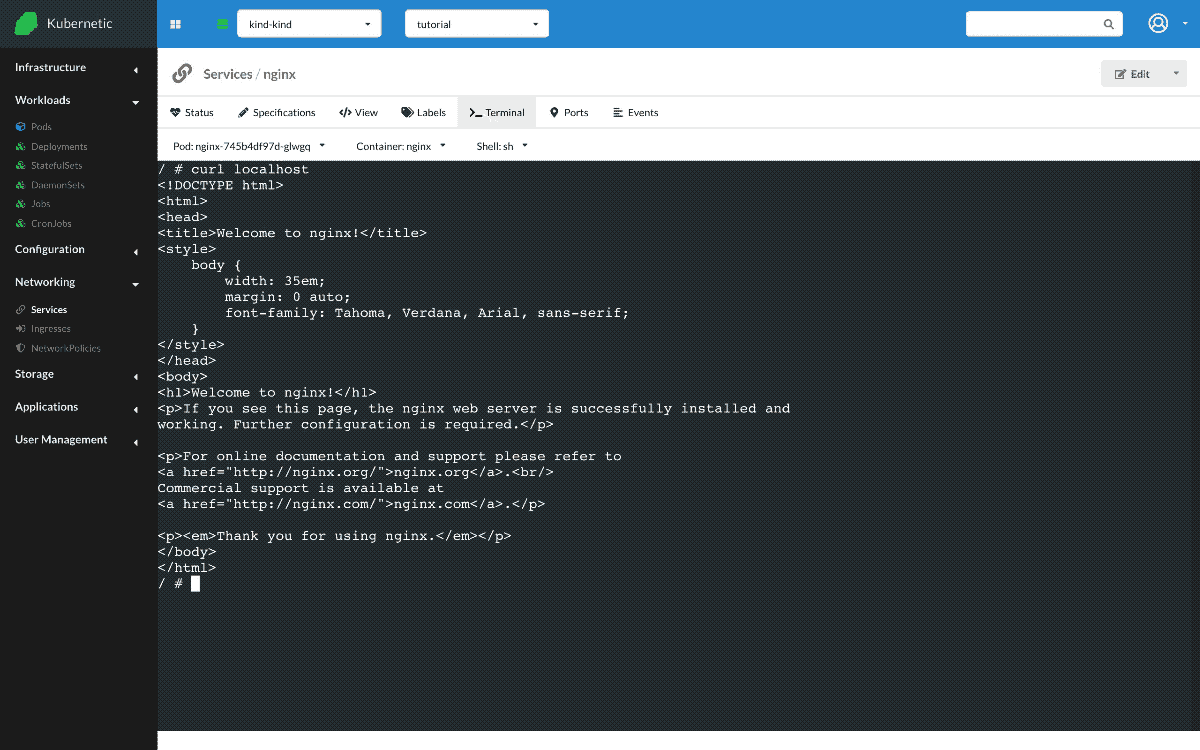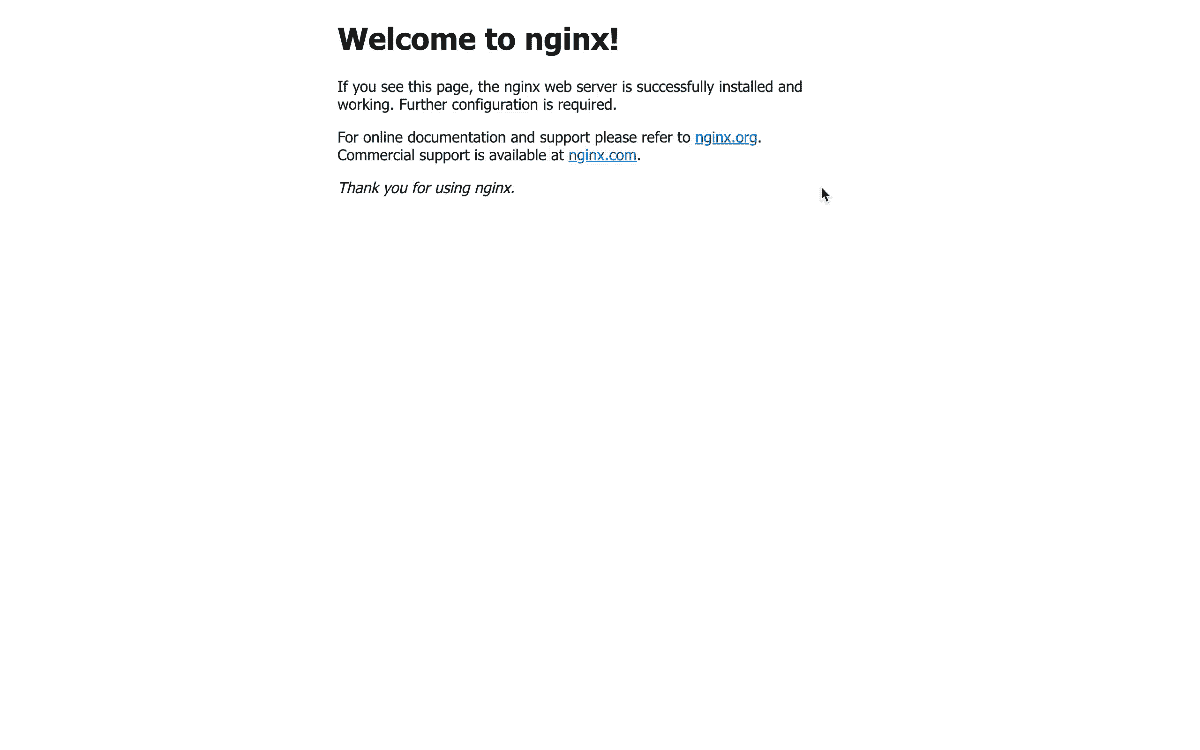
Now that we have the deployment running, let's create a Service of ClusterIP type. ClusterIP service registers an IP on the services subnet and is balancing traffic between the selected set of Pods. Once the Service is up we can see on Status tab that two running Pods are connected to the Service. Let's open a Terminal, this will attach a shell in one of the running Pods. There we run two commands:
curl localhost: Since the command is run inside a runningnginxPod, the running nginx instance in the same Pod responds.curl nginx: The Service is registered in the internal DNS, so when we try to contactnginxthe DNS responds with the Service IP which balances the requests to all running Pods, any one of the two Pods responds.
We can also go to the Ports tab and start port-forwarding to a local port. We can click on the link to view the Service.
ClusterIPservice type is the most restrictive type of Service, as it is only accessible from within the Cluster.
Nginx NodePort Service
- Create:
Service- Name:
nginx - Type:
NodePort - Path:
- Port:
80 - Target Port:
80 - Node Port:
30000
- Port:
- Name:
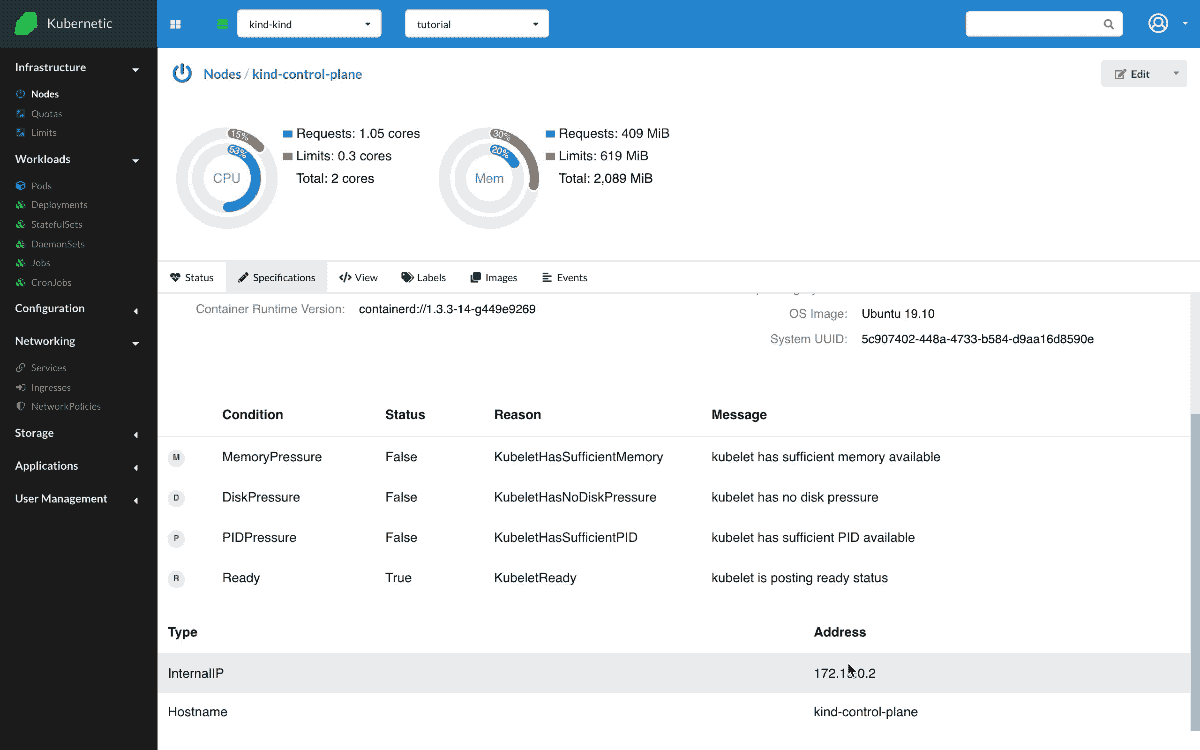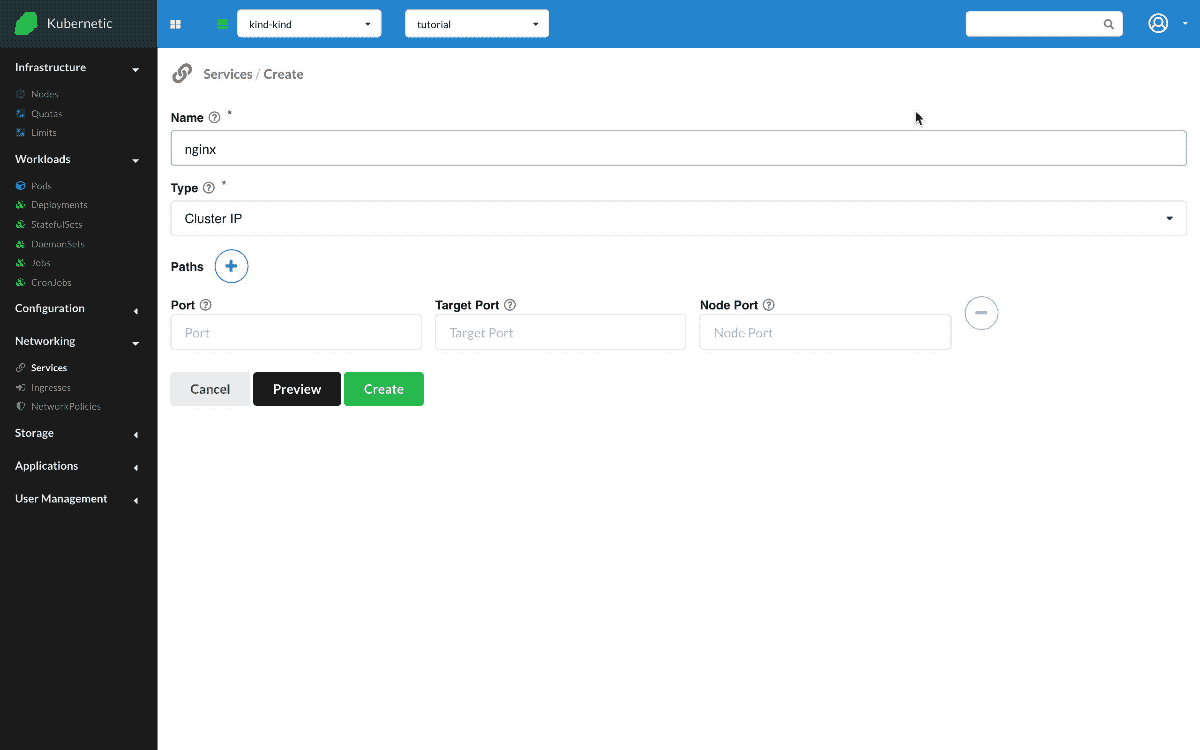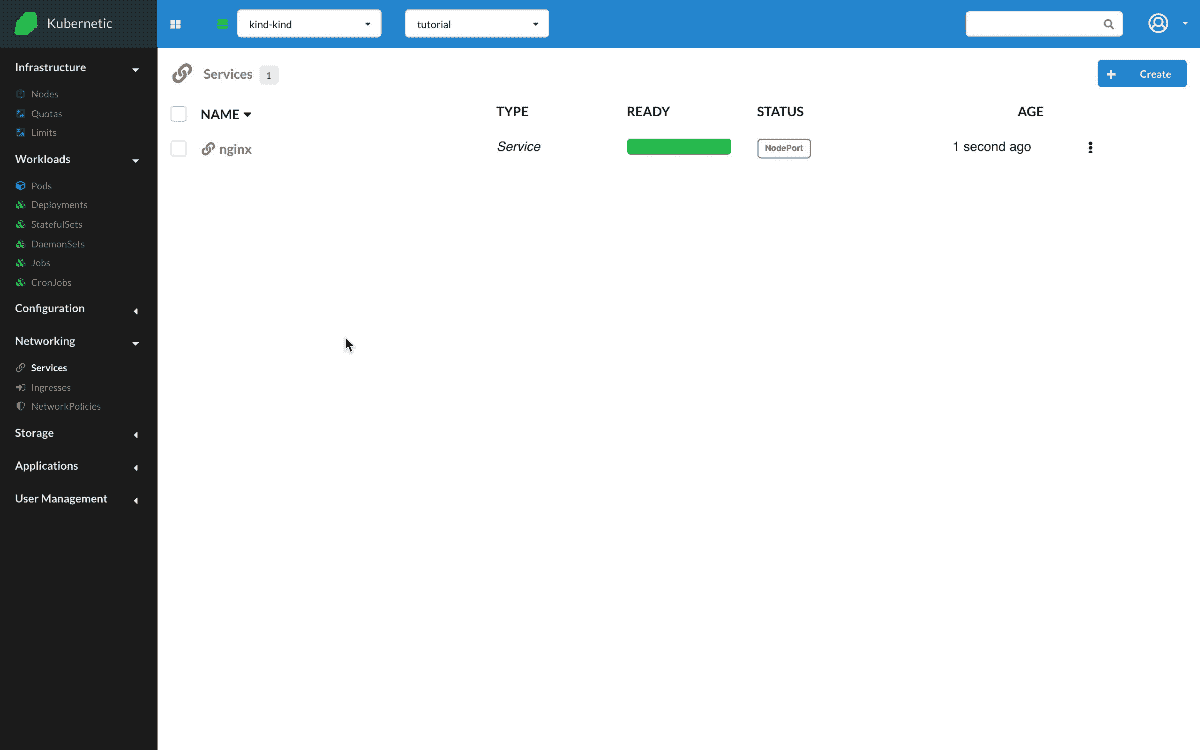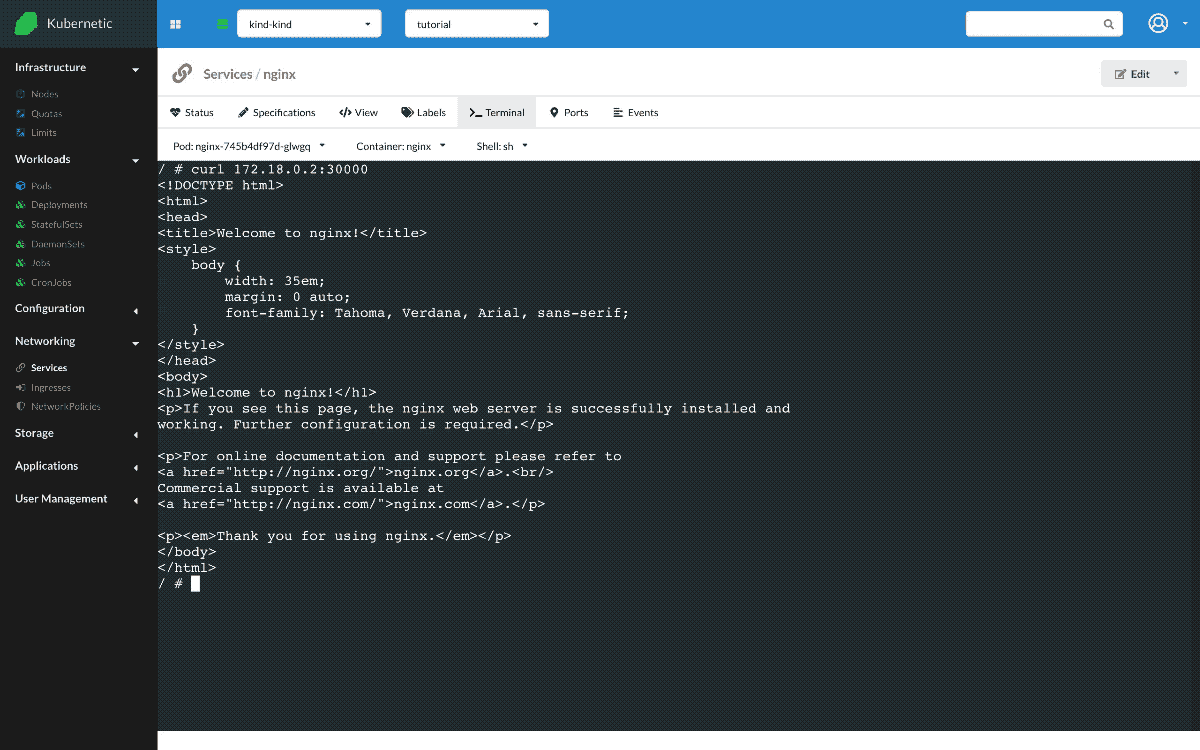
Let's delete previous Service now and instead create a Service of type NodePort. NodePort service exposes a service to a unique node port, on all nodes of the cluster. Let's annotate first the IP of the node, then make sure we have nginx Deployment up and running, and finally create the nginx Service. Once created, we go to the Terminal and try the following command curl <NODE-IP>:30000, the request reaches the service through the node port.
NodePortservice type extendsClusterIPtype by also sending traffic from the node port to the service Cluster IP.
Nginx LoadBalancer Service
- Create:
Service- Name:
nginx - Type:
LoadBalancer - Path:
- Port:
80 - Target Port:
80
- Port:
- Name:
WARNING
In order to create a Service type LoadBalancer you need a Kubernetes provided by a cloud-provider, e.g. GKE.
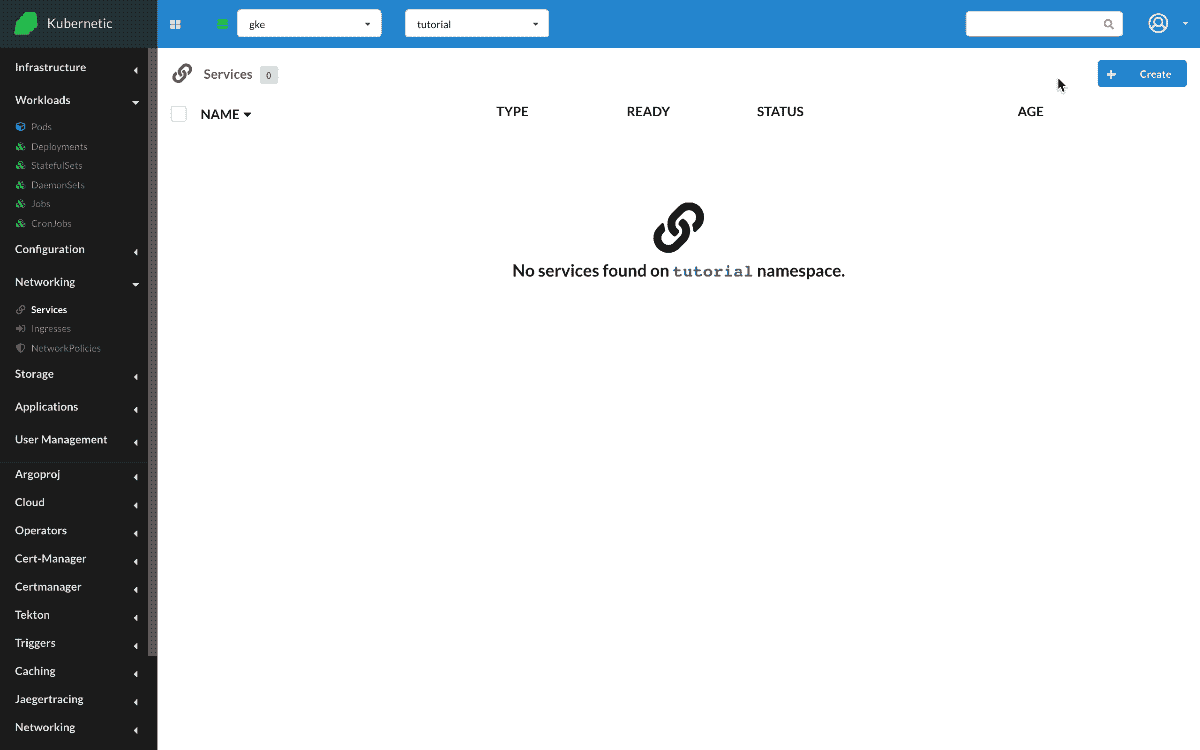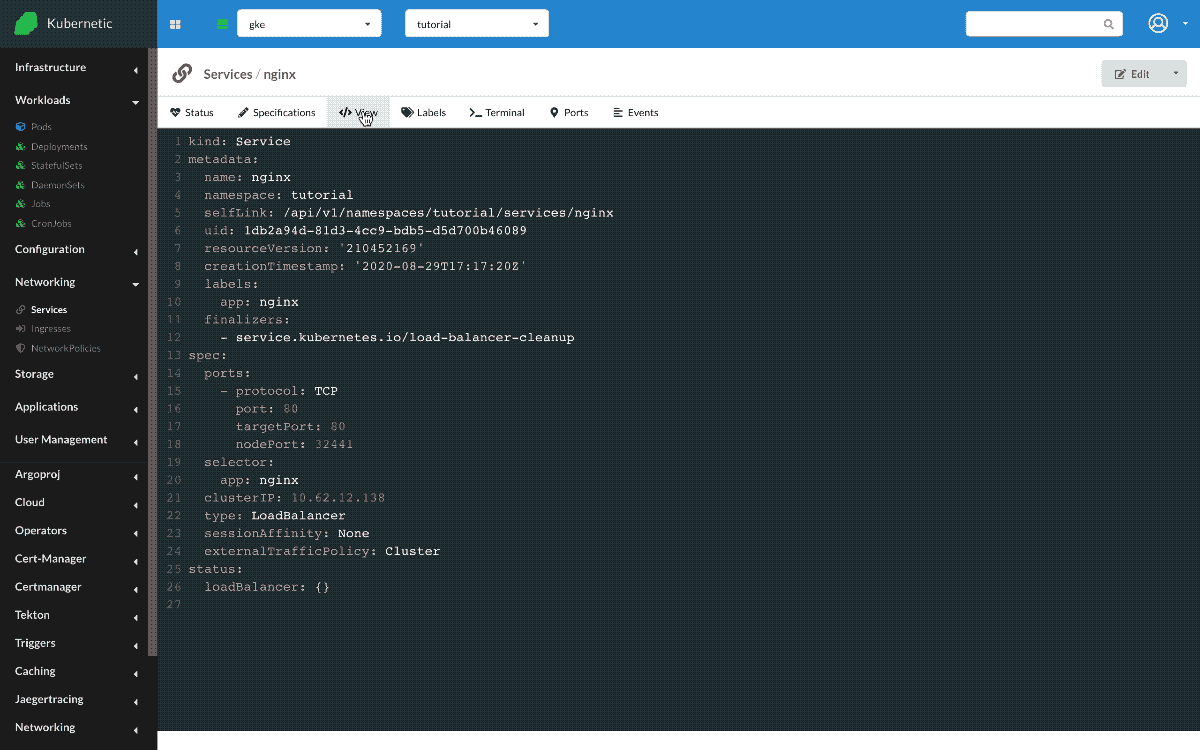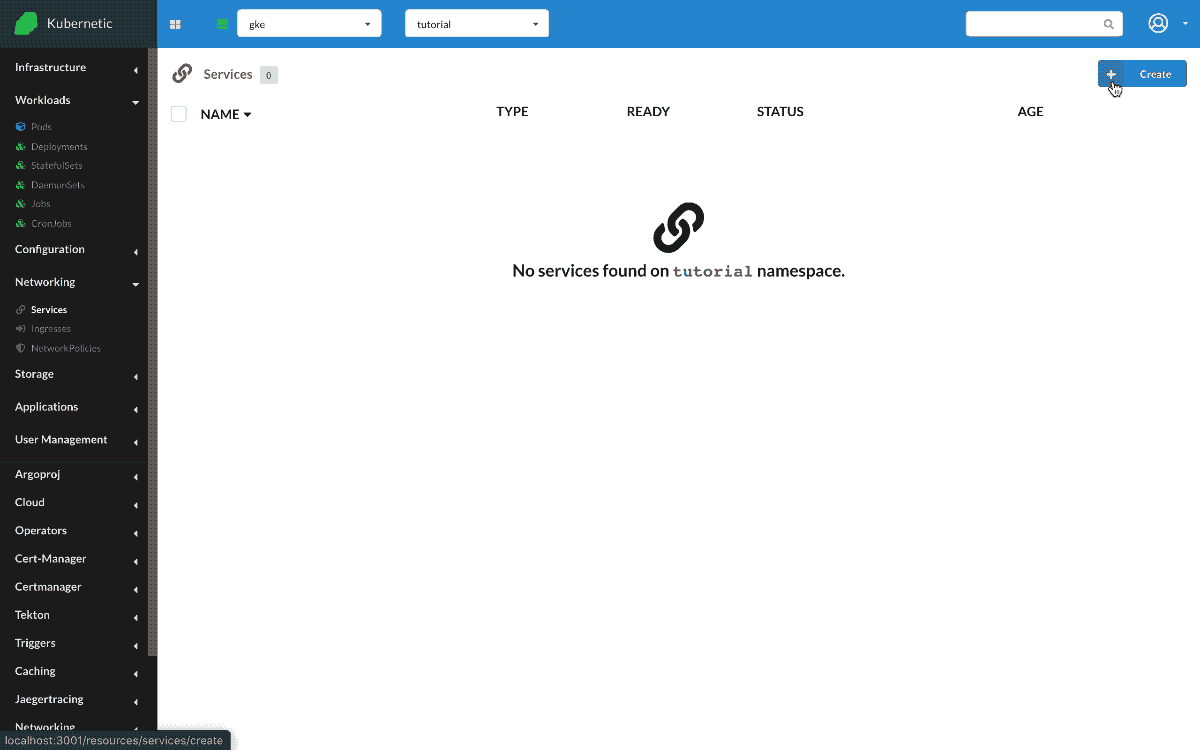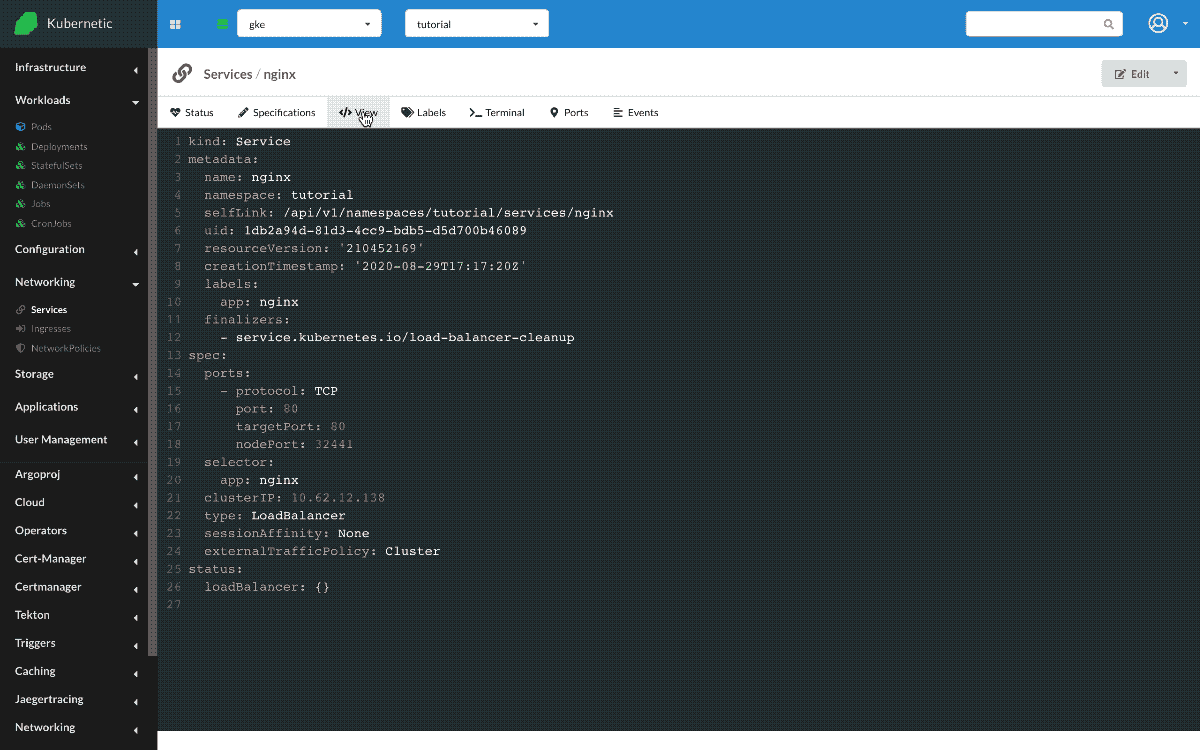
Let's delete previous Service now and instead create a Service of type LoadBalancer. LoadBalancer service exposes publicly the service by instructing an external LoadBalancer to redirect traffic to the Service. The Service will receive a public IP which can then be used to receive requests.
Once created, we go to the Terminal and try the following command curl <EXTERNAL-IP>, the request reaches the service through the external IP.
LoadBalancerservice type extendsNodePorttype by also instructing an external LoadBalancer to redirect traffic to the respective Service.
Cleanup
Remember to delete the following resources after you finish this tutorial:
- on active namespace:
deployments/nginxservices/nginx